WebHooks
When to use?
Webhooks is a feature provided to the merchant, to be notified at a provided url about events, such as payments or refunds. The merchant must submit a url in the relevant form of their EveryPay dashboard. The response of the EveryPay API will be submitted via POST method to provided url.
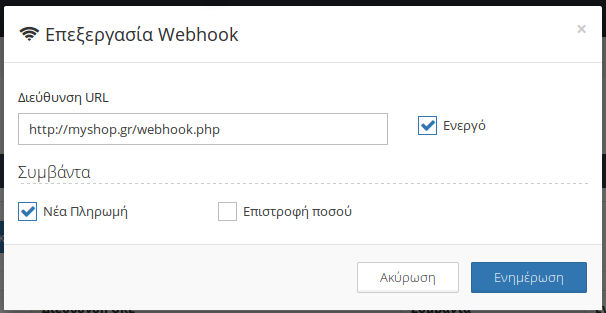
The events that a merchant can choose for webhooks are:
- New payment
- Refund
For example, after a successful payment, the API will send – via POST method – to the url the trader declared a JSON payload, with the following information:
{
"token": "pmt_ETF9EaZURr3l6mC8n6TzClBS",
"date_created": "2015-11-09T19:03:58+0200",
"description": "Order #A-777",
"currency": "EUR",
"status": "Captured",
"amount": 10480,
"refund_amount": 0,
"fee_amount": 272,
"payee_email": null,
"payee_phone": null,
"refunded": false,
"refunds": [],
"installments_count": 0,
"installments": [],
"card": {
"expiration_month": "08",
"expiration_year": "2016",
"last_four": "0003",
"type": "Visa",
"holder_name": "John Doe",
}
...
}
From the above payload, the merchant is able to retrieve useful information regarding this new payment, such as the token, the date of the transaction, the amount, any refunds, installments, and non-sensitive card details used for the transaction (the last 4 digits, the cardholder name, etc).
Installation
Go to your account settings page from the Dashboard interface (https://dashboard.everypay.gr) – after logging in with your credentials. Select Webhooks from the account settings page.
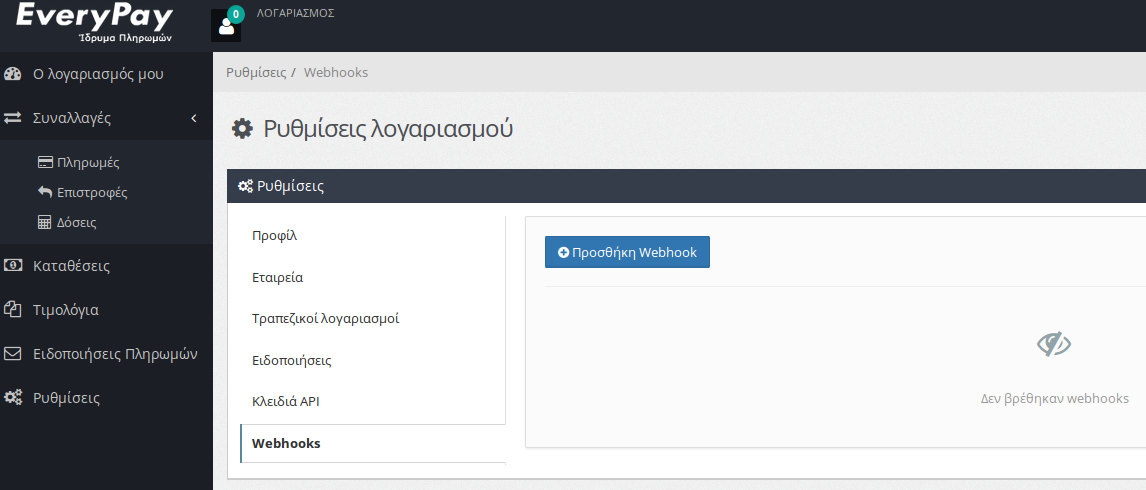
You may add many webhooks, but only one for each event. If you submit multiple webhooks for the same event, only the last one will be active. Just submit the url and the type of event for that webhook.
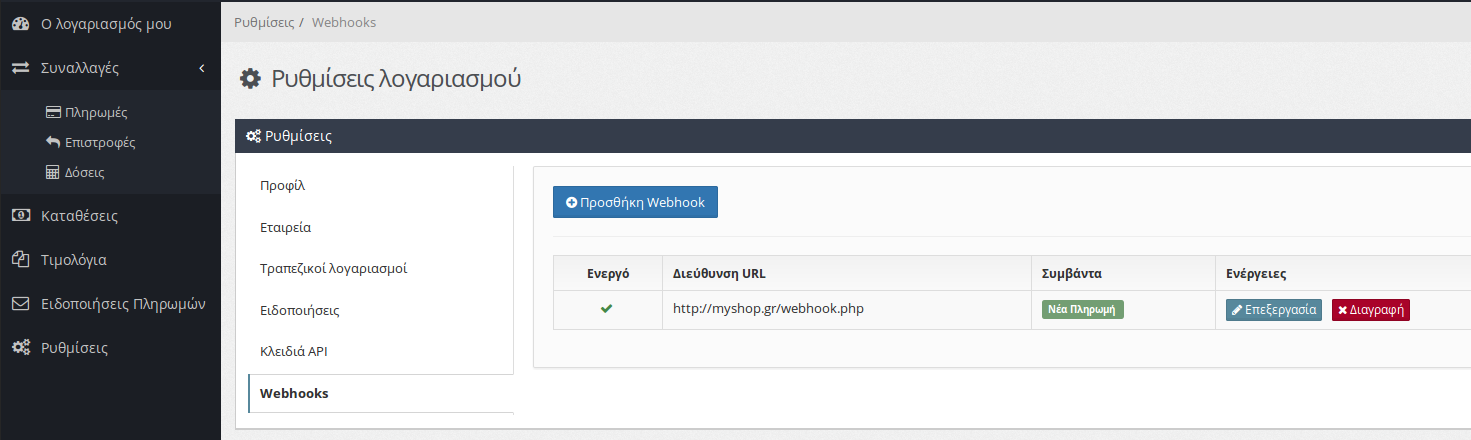
You can manage your webhooks from the list at any time, as shown below.
Warning: Make sure that your service will not block requests from the following IP addresses, as these are the EveryPay servers that will send the webhook notifications:
- 3.72.230.60
- 3.126.178.16
- 3.124.245.137
Signature Validation
To ensure the authenticity and integrity of webhook requests, each request includes a signature in the X-Signature-SHA256 header.
This signature is generated by hashing the JSON payload with your API secret key using the HMAC-SHA256 algorithm, and then encoding the result in base64.
How the Signature is Generated
- The payload (request body) is JSON-encoded without extra spaces or formatting.
- The signature is calculated as:
base64_encode(hash_hmac('sha256', $payload, $secretKey));
$payloadis the exact JSON string sent in the request body.$secretKeyis your API secret key.
The resulting signature is sent in the X-Signature-SHA256 HTTP header.
How to Validate the Signature (PHP Example)
<?php
$secretKey = 'YOUR_SECRET_KEY'; // Replace with your actual secret key
// Get the raw POST body
$input = file_get_contents('php://input');
// Get the signature from the header
$signature = $_SERVER['HTTP_X_SIGNATURE_SHA256'] ?? '';
// Compute the expected signature
$computedSignature = base64_encode(hash_hmac('sha256', $input, $secretKey));
// Compare signatures
if (hash_equals($computedSignature, $signature)) {
// Signature is valid
http_response_code(200);
echo json_encode(['success' => true]);
} else {
// Signature is invalid
http_response_code(401);
echo json_encode([
'error' => 'Unauthorized',
'message' => 'Signature validation failed'
]);
}
Payment Notification webhooks
Payment Notification webhooks notify your system when the status of a Payment Notification Link changes.
Use these events to keep your internal systems in sync with customer actions, update invoice or order state, and trigger reconciliation or follow-up flows.
Notification paid
Triggered when a Payment Notification is successfully paid by the customer.
At this point:
- the notification status transitions to
paid - a Payment object has been created
- the payment can be safely fulfilled and reconciled
Recommended usage
- Mark the related invoice or order as paid
- Reconcile the payment using the notification token and metadata
Payload example
{
"split": false,
"token": "pnt_0fNkCao2MHU7S7ywHj9OCHOq",
"amount": 1000,
"locale": "el",
"status": "Paid",
"payment": "pmt_HtBAwSe0P3JxZHBTN72gGPcY",
"metadata": [],
"payee_name": "John Smith",
"description": "Η πληρωμή σας για την παραγγελία 007392",
"payee_email": "john.smith@everypay.gr",
"payee_phone": 6990000000,
"skip_notify": true,
"date_created": "2026-01-21T09:57:03+0200",
"create_customer": false,
"expiration_date": "2026-01-23T07:57:03+0200",
"payment_link_url": "https://dashboard.everypay.gr/pay/pnt_0fNkCao2MHU7S7ywHj9OCHOq"
}
Notification expired
Triggered when a Payment Notification expires before payment is completed.
At this point:
- the notification status transitions to
expired - the payment link is no longer usable
Recommended usage
- Mark the payment request as expired
- Create and distribute a new payment notification if payment is still required
Payload example
{
"split": false,
"token": "pnt_0fNkCao2MHU7S7ywHj9OCHOq",
"amount": 1000,
"locale": "el",
"status": "Expired",
"payment": null,
"metadata": [],
"payee_name": "John Smith",
"description": "Η πληρωμή σας για την παραγγελία 007392",
"payee_email": "john.smith@everypay.gr",
"payee_phone": 6990000000,
"skip_notify": true,
"date_created": "2026-01-21T09:57:03+0200",
"create_customer": false,
"expiration_date": "2026-01-23T07:57:03+0200",
"payment_link_url": "https://dashboard.everypay.gr/pay/pnt_0fNkCao2MHU7S7ywHj9OCHOq"
}